Archives
Baby is 15 months – walking & talking – what we can say and do
…

Look at my cool yellow hat
The baby (or is it toddler now?) is 15 months! He’s been talking more and is now walking fully – when I say fully, i mean he’s walking everywhere and not resorting to any crawling. However, his walking is still a bit robotic and jerky, cowboy-esque.
Here’s some words I’ve noticed he can say, appropriately and in context, although not all of them are clear:
-
thank you (clear; one of his first words)
-
daddy (very clear)
-
pea (very clear; he likes peas)
-
sock(s) (clear)
-
banana (but not very clearly)
-
attempts to say “open” but not clear at all
-
down (clear; put me down – is confusing up and down though, mainly just says “down” for wanting both to be picked up and put down)
-
sit down (clear; he likes to sit on the sofa)
-
wow (very clear)
-
wee wee (very clear; and will go sit on the potty – has probably been influenced by his brother’s potty training, also see here and here for more on potty training)
-
poo (clear)
-
apple (clear; one of his first words)
-
Sarah duck (kind of clear; a kid’s cartoon he and his brother like to watch about a girl called Sarah and her friend, a duck)
-
ball (not very clear)
-
twinkle twinkle (and can sing more of the song including up above the world so high, not very clear)
-
round (kind of clear – relates to wheels on the bus song)
Next development step with talking: putting two words together!! (not including wee wee)…
First words, first steps and (nearly) first birthday baby
…

I can talk and walk now! (nearly)
Ever noticed your baby/child becomes a little more grumpy, more difficult to settle, get to sleep, more crying etc just before a big developmental change? A week or so ago the baby (nearly 12 months old) needed a lot of help getting to sleep. He cried and cried if I dared put him down in his cot. I had to hold him, rock him, sit down next to the cot and pat his back until he fell asleep. He didn’t want to nap and was quite grumpy.
Big changes were afoot
So a few days ago we think he said his first word. He appeared to use it in context and appropriately. His first word was…
“Up”
Then today, he took his first steps! Haven’t been able to get him to re-create this however. The toddler I remember was quite uncertain around walking at first, but after a few tries his walking really sped on. So here’s to crazy baby and toddler running up and down the corridors!
Tummy Time for baby – and why it’s important
 …
…
Tummy Time (TT) is important in that long road toward crawling and eventually walking. It involves baby working their muscles, coordination skills and learning to push up, sit up, roll over and other gross motor skills. It’s therefore important to give babies time on their tummy.
Since the Back To Sleep campaign (babies to sleep on their backs), babies were apparently getting less “tummy time” during the day, leading to some delays in reaching important developmental milestones such as crawling (according to this article from the BBC on the importance of Tummy Time for babies and their development). These children did catch up, however.
Some babies can really dislike tummy time, however. I found some tips on this site from a paediatric occupational therapist
– 7 tips for making tummy time a little less miserable, if TT needs some encouragement.
-
It writes about 7 steps to independent TT, starting each step a few times a day for a few minutes while progressing up the steps. It’s also a good idea not to do TT too soon after a meal otherwise there might be a bit of spit up.
-
The Little Lovely (LL) didn’t really mind TT, although in the first few months he could only tolerate a short amount of time on his tummy before making frustrated sounds. I think this was because he was working quite hard in trying to do mini push ups and so it was probably quite tiring for him.
There is a wealth of information out there on how to make tummy time fun and interesting for you both, how to assist baby with tummy time and what to do if baby does not like being on this tummy.
When I first started with LL we tried some assisted TT by rolling up a towel or blanket and putting this under his chest so that he could experience his chest being raised and pushed up from the floor, but without so much of the strain for him.
-
Make it a bonding experience – there are different games you can play while practising TT and baby doesn’t have to be on their own, tummy down on the floor. Try placing baby on your tummy, tummy to tummy so that you can both see each other when they lift their head. Or, lie on your back and put baby on his tummy on your legs.Lift up your legs, while holding baby securely, and pretend to be an aeroplane. If baby is tummy down on the floor, use toys to encourage them to reach, move, and lift their head. Or, talk or sing to your baby to encourage this. Always supervise TT with baby.
Some useful links:
-
-
How to make tummy time more fun for your baby – some tips including “forget the floor”, “prop up”, “face to face” and “make it fun”, from a website where the authors are “moms and pediatric therapists”
-
The “ultimate guide to happy tummy time”, from CanDoKiddo, written by a “pediatric occupational therapist”. Lots of links to her articles, tips, and a handy short video of tummy time tips. Great!
-
First days of weaning the baby (we are 6 months old)
…

The first week of weaning: what we ate and why
So, we are 6 months old!
I tried to go away for the weekend. The baby did not like it. He wanted to be fed and wanted me there. I had to come back slightly early. Then I realised (slight second baby syndrome related delay about this) that hey he’s 6 months now and so I should think about weaning (also known as “complementary feeding”, CF).
When is baby ready for solids?
The NHS writes that:
Every baby is an individual, but there are three clear signs that, together, show your baby is ready for solid foods… It’s very rare for these signs to appear together before your baby is six months old.
1. They can stay in a sitting position and hold their head steady.
2. They can co-ordinate their eyes, hands and mouth so they can look at the food, pick it up and put it in their mouth, all by themselves.
3. They can swallow food. Babies who are not ready will push their food back out with their tongue, so they get more round their face than they do in their mouths.
(http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/pages/solid-foods-weaning.aspx)

What you feedin’ me?
Where to start?
Question: How do you get your child to eat vegetables?
Answer: …feed them vegetables!
Some research suggests introducing vegetables in the first few weeks of weaning. Infants may be more willing to try and like new vegetables if vegetables are offered in the first few weeks of weaning – a variety of vegetables, both bitter and sweet, and trying each one a few times because baby may initially dislike or refuse to taste it (as discussed in this article here by Nicola Slawson, 2015). One study (3) reported that
Early exposure to a rotation of vegetable flavours first added to milk then to cereal increased intake and liking of these vegetables during CF [complementary feeding]
Why start with vegetables? – The first few years of life are important in terms of developing healthy eating habits (1) and new foods are more readily accepted in those early years (2). Once a food habit is established they tend to be quite stable (3). So introducing vegetables at the start of weaning/CF might make it more likely for the child to like and accept vegetables as they grow older
Several studies have now shown that CF with vegetables facilitates liking and intake of vegetables compared to CF with fruit (a, b, cited in Hetherington et al. 2015)
What helps a kid to like vegetables? Hetherington and colleages (3) report on different methods such as “stealth” to disguise vegetables in food, or adding other flavours that the child already likes. However, the most successful strategy in promoting vegetable eating is
Mere or repeated exposure…
…Early and repeated experience with vegetables serves to increase acceptance
So basically, giving them the vegetables, again and again, to promote “familiarity” (4) and “learned safety” (5). Vegetable presentation needs to be rotated with daily variety, in addition to the exposure (6). Hetherington et al (3) also report that adding vegetables to familiar and liked foods such as milk and cereal facilitated intake and liking of the vegetable. Adding milk to the vegetable can reduce any bitter or sour tastes due to the sweetness in the milk (both breast and formula milk) and dilution effect of adding it (3).
Our first foods
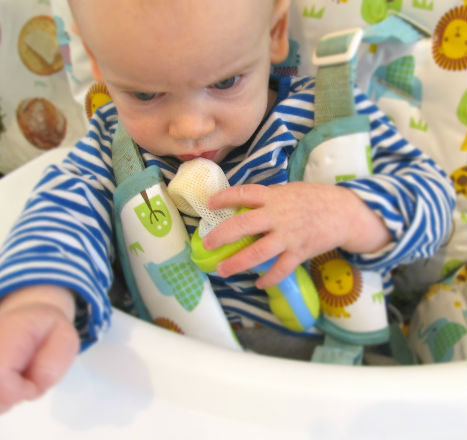

Banana in a mesh self feeder
We started with baby rice mixed with his usual milk. In the first week we then moved on to a few spoonfuls of:
-
Cauliflower purée (mixed with his usual milk)
-
Avocado (in a mesh self feeder, see picture)
-
Banana (yeah I know this isn’t a vegetable but it was easy to put in the mesh self feeder)
-
Parsnip purée
Future planned foods for week 2:
-
Broccoli
-
Carrots
-
Potato
-
Butternut squash

Cauliflower Purée
The weaning plan (read more on this useful sheet here):
-
Offer one vegetable at a time
-
Offer a variety of vegetables (because of issues as discussed above)
-
Repeated exposure, to vegetables! Keep trying and offer the food a good few times even if baby doesn’t seem to like it at first (increases chance that baby will eventually accept the food (7) )
References:
References 1-6 cited in Hetherington et al., 2015:
- Cashdan, E. (1994). 1994. A sensitive period for learning about food. Human Nature, 5 (3), pp. 279–291
- Lange, M. Visalli, S. Jacob, C. Chabanet, P. Schlich, S. Nicklaus. (2013). Maternal feeding practices during the first year and their impact on infants’ acceptance of complementary food. Food Quality and Preference, 29 (2), pp. 89–98.
- Hetherington, M. M., Schwartz, C., Madrelle, J., Croden, F., Nekitsing, C., Vereijken, C.M.J.L. & Weenen, H. (2015). A step-by-step introduction to vegetables at the beginning of complementary feeding: The effects of early and repeated exposure. Appetite, 84, pp. 280–290
- Zajonc, R.B. (1968). Attitudinal effects of mere exposure. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, Monograph Supplement 9 (2 Pt. 2), pp. 1–27.
- Kalat,J. W. & Rozin, P. (1973). Learned safety” as a mechanism in long-delay taste-aversion learning in rats. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 83 (2) (1973), pp. 198–207.
- Nicklaus, S. (2011). Children’s acceptance of new foods at weaning. Role of practices of weaning and of food sensory properties. Appetite, 57 (3), pp. 812–815
- Maier, A. et al. (2007). Effects of Repeated Exposure on Acceptance of Initially Disliked Vegetables in 7-month Old Infants. Food Quality and Preference 18(8): 1023-1032.
a) Barends, J. de Vries, J. Mojet, C. de Graaf. (2013). Effects of repeated exposure to either vegetables or fruits on infant’s vegetable and fruit acceptance at the beginning of weaning. Food Quality and Preference, 29 (2), pp. 157–165
b) Remy, S. Issanchou, C. Chabanet, S. Nicklaus. (2013.) Repeated exposure of infants at complementary feeding to a vegetable puree increases acceptance as effectively as flavor-flavor learning and more effectively than flavor-nutrient learning. The Journal of Nutrition, pp. 1194–1200
Tooth for the price of one – again! (teething, biting & breastfeeding)
So I thought I could see a new tooth coming in on the top, an “upper central incisor”. This would be the next tooth to come in after his lower front teeth according to tooth order information. However, yesterday it looked like, again, he decided to be efficient and grow two at the same time. And yes, indeed there is another upper central incisor coming in. So now we will have a scary mouth of upper and lower front teeth. Scary for me as I am the one feeding him. He has bitten me twice; I had already thought in advance what I was going to do if he bit me. I decided to yell and express that it hurt as soon as he bit me, to take him off, look at him and say “biting hurts mummy” – see this post on behavioural psychology and explanation of reinforcement and punishers for why – in a nutshell, I wanted to give immediate feedback and a consequence to the biting, and to show that it had an impact. He cried and I cuddled him.
Here’s a brief recap on punishment and reinforcement:
- “Punishment” doesn’t necessarily mean there is a harmful or dangerous consequence, it’s a process where a consequence immediately follows a behaviour which decreases the future likelihood of that behaviour occurring. Positive punishment is where a negative consequence is put in place after the behaviour, like sending child to “time out” or telling them off, and negative punishment where a good thing or desired outcome is removed after the behaviour occurs, such as removing cake/sweets.
- Reinforcement is where behaviour increases. Positive reinforcement is where a behaviour increases because it’s followed by a positive/motivating consequence. Negative reinforcement is where behaviour increases because a negative consequence is removed, such as a kid does his chores (behaviour) to avoid being nagged to do it (negative).
So I suppose expressing my discomfort would be a positive punisher? I don’t know if it was the “right” thing to do but I don’t want to be bitten and in fear at every feed. It seemed to work and there was no biting again for a few weeks, then he bit slightly a few days ago, so I did the same thing. I don’t know if that was because he had a new tooth coming in and he was experimenting, or what.
Also, the Little Lovely (LL) appears to be teething a bit earlier than average; first teeth might not come in until between 5 and 7 months, according to this page on teething from the NHS, and upper central incisors at 6 to 8 months. LL was about 4.5 months when his first teeth came in so maybe his younger age impacts on biting and feeding issues? I don’t really know, I’m just thinking out loud.
What I noticed each time, however, is that he was not really eating and had probably finished. It feels like sometimes, toward the end of the feed he is just “mucking around” a bit. I can tell this by playing with his hand or kissing on his arm. If he has finished eating then he will giggle a bit and smile – if he is proper eating and seriously concentrating on that, he does not react to this playing so I leave him to get on with eating. So, maybe he was just experimenting with his new teeth. I will need to retrospectively complete a behavioural analysis on the situation if he does it again! Indeed, from from having a quick search online babies are more likely to bite if they are full, and teething can also impact on biting. So looking at contextual factors in considering why baby bites might be helpful because LL was teething when he bit a few days ago because the other top front tooth was probably about to break through.
Here are some “tips to reduce and eliminate biting” from La Leche League (LLL). In summary, they write:
- it’s physically impossible for baby to bite when latched on correctly and nursing actively. this is because baby needs to stop sucking in order to bite – so this supports my observation that his biting came at the end of the feed when he was “mucking about” and not actually eating as actively as he does at the start of a feed
-
So, as a first “hint” of when your baby is about to bite, try and watch for a moment–usually after the initial hunger has been satisfied–when your nipple slips forward in your baby’s mouth. Often the tension in your baby’s jaw will change just before this happens.
- when you notice this “change”, you can release the suction by placing a finger into the corner of baby’s mouth and take him off, keeping your finger in his mouth to protect the nipple. Pulling baby off might seem like an automatic response to being bitten, but it will be less painful if you release the suction!
- positioning may be relevant: pull baby in closer. If he begins to position himself away from the nipple, “be alert for a possible bite”. Great
See here for further information from LLL on “if your baby bites”, an interesting page that offers more details to the above points on what to do if baby bites, factors that might contribute to biting, positioning matters, preventing biting and gaining perspective. The contributing factors section is interesting; it’s helpful to think about what is contributing to the biting when attempting to address it. For example, the page writes that colds (lack of clear airway could interfere with suckling correctly) teething and asking for attention can be contributing factors. Responses to and attempts to address biting might be different depending on different contributing factors.